Simulation of Microstrip Patch Antenna using HFSS software with analysis of rectangular plot, polar plot and smith chart.
Microwave
Engineering Lab (BTEC-606)
Experiment
No: 2
AIM: Simulation of Microstrip Patch
Antenna using HFSS software with analysis of rectangular plot, polar plot and smith chart.
SOFTWARE
USED: ANSYS HFSS 15.0.3
THEORY:
Microstrip Patch Antenna: A patch antenna (also known as a rectangular
microstrip antenna) is a
type of radio antenna with
a low profile (small
height and width), which
can be mounted on a flat surface. It consists of a flat rectangular sheet or
"patch" of metal,
mounted over a larger sheet of metal called a ground plane.
In telecommunication, a microstrip antenna (also
known as a printed antenna)
usually means an antenna fabricated
using microstrip techniques on a printed
circuit board (PCB). They are mostly used
at microwave frequencies. An individual microstrip antenna consists of a patch of
metal foil of various shapes (a patch antenna) on the surface of a PCB, with a metal foil ground
plane on the other side of the board. Most
microstrip antennas consist of multiple patches in a two-dimensional array. The
antenna is usually connected to the transmitter or receiver through
foil microstrip transmission
lines. Microstrip antennas have become very popular
in recent decades due to their thin planar profile which can be incorporated
into the surfaces of consumer products, aircraft and missiles, their ease of
fabrication using circuit techniques, the ease of integrating the antenna on the same board with
the rest of the circuit, and the possibility of adding active devices such
as microwave integrated circuits to the antenna itself to make active
antennas.
Procedure:
NOTE: Only after the completion of 1st experiment, you can start this 2nd experiment from following steps:
Here is the link of 1st Experiment.
1.
Select air-
press F (Then select the face)
2.
Go to
edit-select-By name
3.
Select air
(select the faces except bottom face)
4.
Go to
HFSS
5.
Boundaries-assign-radiation
6.
Name:
Radiation ok
7.
Save the
file
8.
Go to
analysis
9.
Add
solution
10. Solution frequency= 7.5 Ghz
11. Adaptive solution
12. Maximum number of passes: 20
13. Maxm deltas= 0.02 ok
14. Then analysis setup 1-right click-add frequency
sweep
15. Sweep type: fast
16. Frequency setup
17. Type: linear step
18. Start: 5 Ghz
19. Stop: 10 Ghz
20. Step size: 0.1 Ghz
21. untick the save field ok
RUN THE PROJECT:
1.
Result-
create modal solution data report-rectangular plot
2.
Category:
sparameter
3.
Function:
db
4.
New report
5.
Close
FOR RADIATION PATTERN:
1.
Result –
Create far fields Report - Radiation pattern
2.
Category:
rE
3.
Quantity:
rE total
4.
Function:
dB
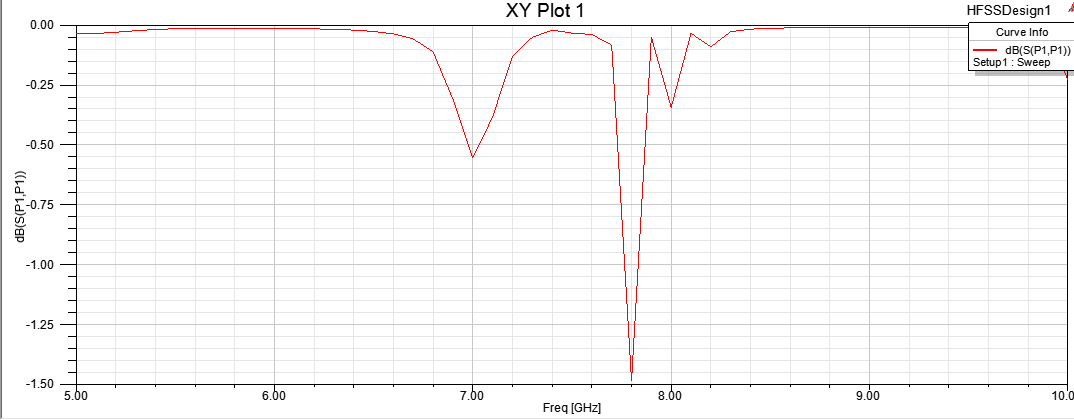
Figure: Rectangular plot
Figure: 3D polar plot
Figure: Smith chart



Comments
Post a Comment